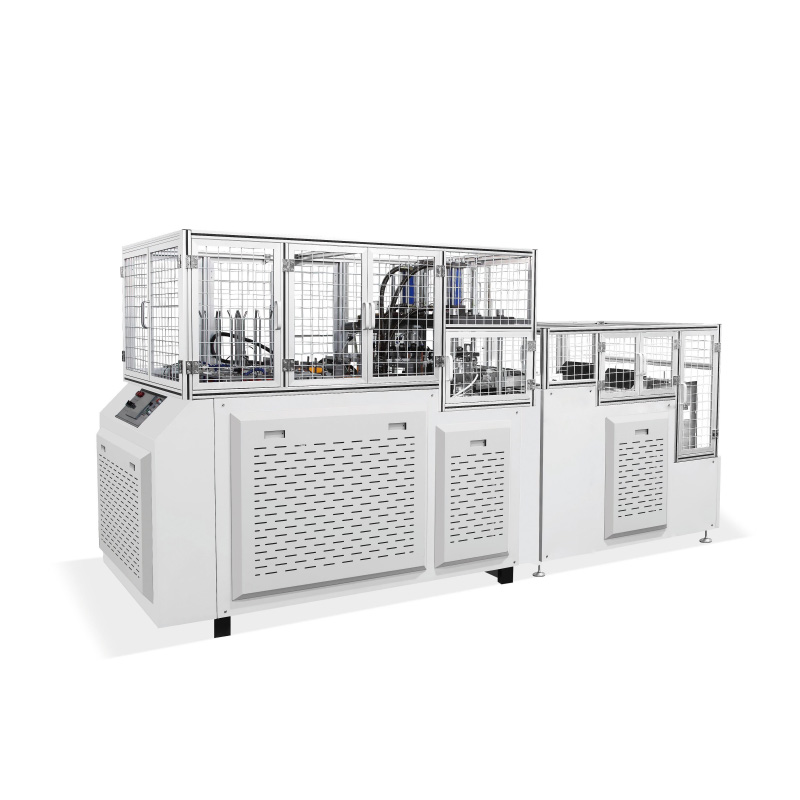
As global demand for pre-packaged meals, corporate catering, and school lunches surges—driven by busy lifestyles and the ready-to-eat (RTE) food sector growth—manual lunch box production has become a bottleneck for many food businesses. Slow speeds, inconsistent quality, and high labor costs hinder scalability. The automated lunch box making machine solves these pain points, streamlining production while ensuring food safety and standardization. Below is a simplified breakdown of its functionality and key value for catering companies, prepared meal factories, and institutional food suppliers.
Why Automated Lunch Box Making Machines Are Gaining Traction
A 2024 Global Food Service Association report notes 78% of catering businesses list “lunch box production efficiency” as their top operational challenge. Manual processes (assembling, filling, sealing, labeling) typically handle 150–200 boxes per hour, with 10–15% waste from human error (e.g., lopsided filling, broken boxes).
Automated machines address these issues, especially as food safety regulations (FDA’s Food Safety Modernization Act, China’s GB 4806) tighten. For small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) targeting corporate or institutional catering, this equipment has shifted from “nice-to-have” to “must-have.”
How Automated Lunch Box Making Machines Work
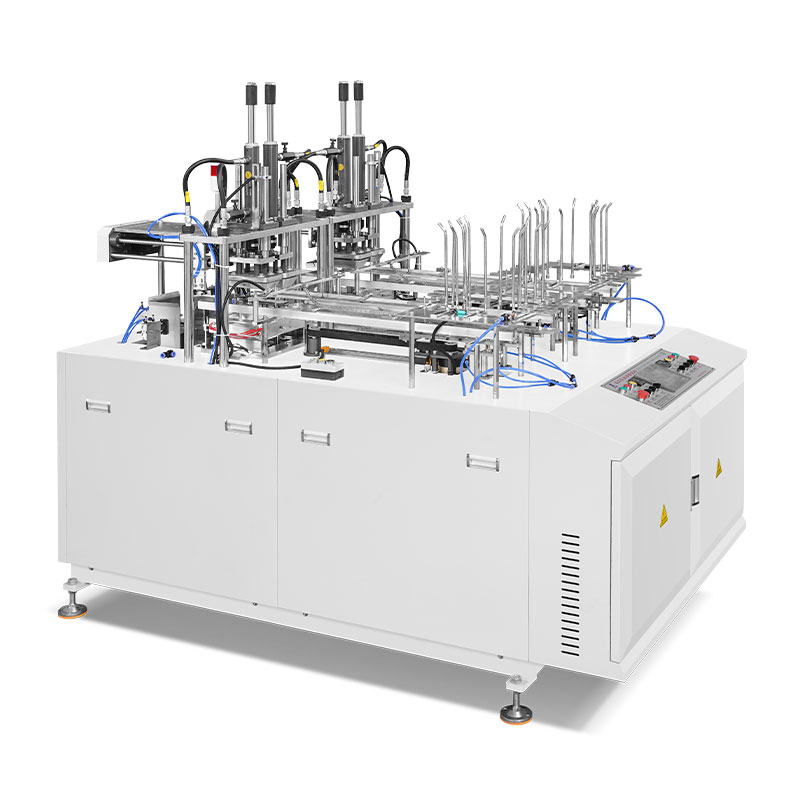
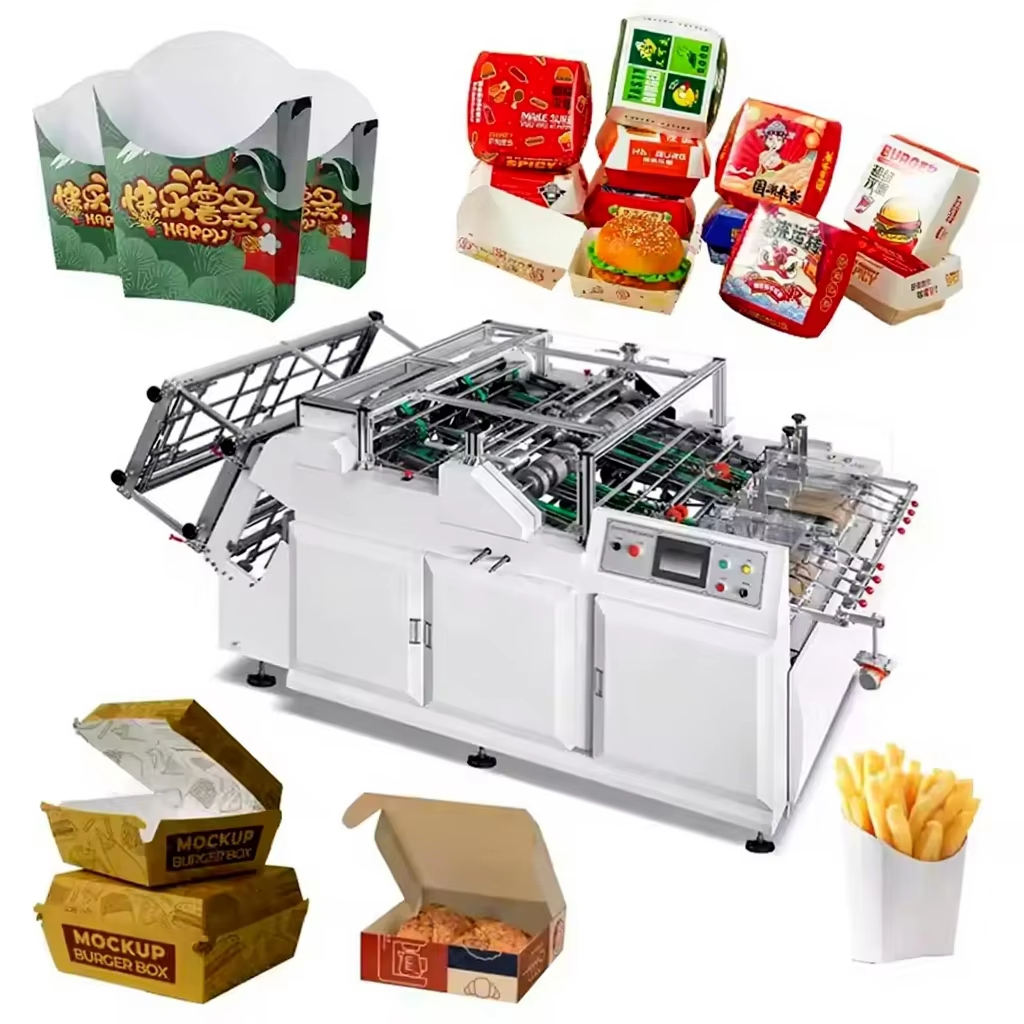
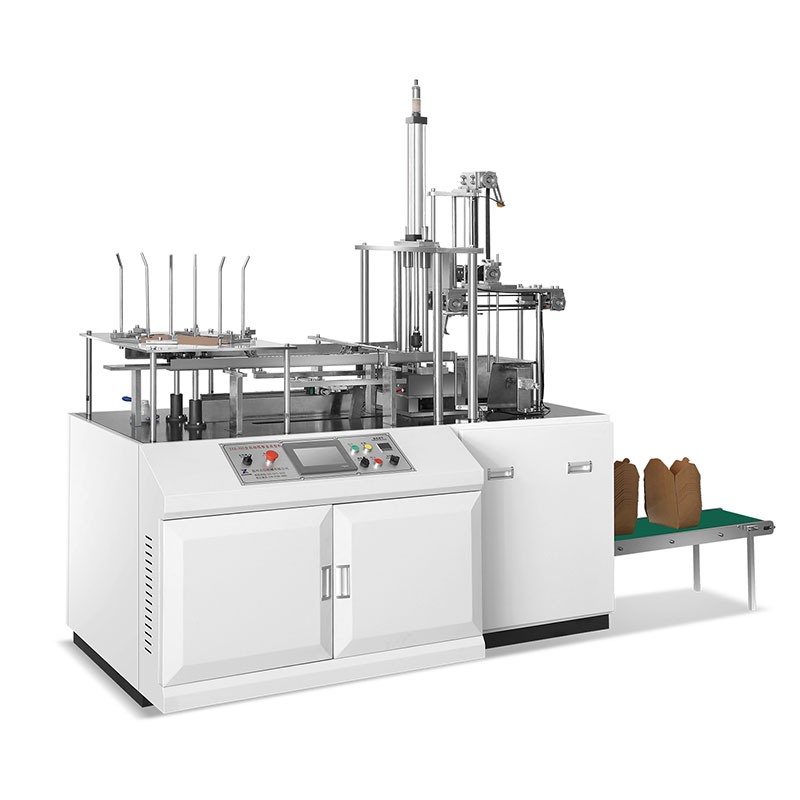
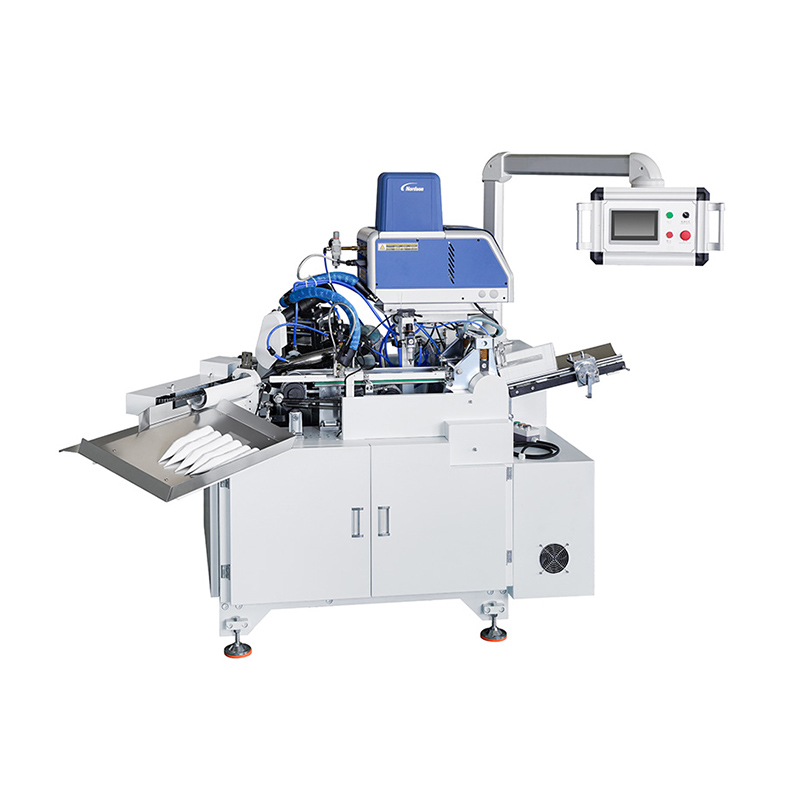
Automated lunch box machines integrate 4 core functions into one PLC-controlled system for precision. The workflow begins with raw material feeding: flat, food-grade materials (PP plastic, biodegradable PLA, paperboard) enter a forming station, where heat/pressure (or vacuum forming) shapes them into custom-sized lunch boxes (3-compartment, 4-compartment, etc.) to separate rice, veggies, and protein.
Next, the filling station dispenses pre-cooked food via multiple nozzles (for different food types), with weight sensors ensuring consistent portions (e.g., 150g rice, 100g veggies) to control costs and satisfy customers. After filling, the sealing station uses heat or ultrasonic technology to attach lids, creating an airtight seal that extends shelf life (1–2 days to 3–5 days for refrigerated meals), prevents leakage, and blocks contaminants—some models add nitrogen flushing for crisp foods.
Finally, a quality control station with AI visual sensors checks for unsealed boxes, incorrect portions, or damaged lids (rejecting faulty units automatically), while integrated labeling modules print expiration dates, batch numbers, and logos—eliminating the need for separate labeling equipment.
Core Benefits for Catering & Food Businesses
Automated lunch box machines deliver tangible value for businesses of all sizes, starting with efficiency: manual teams handle 150–200 boxes/hour, while semi-automatic models reach 800–1,200 boxes/hour and fully automatic versions hit 1,500–2,000 boxes/hour. For a caterer serving 5,000 employees daily, this cuts production time from 8 hours to 2–3 hours.
Cost savings are equally impactful: replacing 3–4 manual workers with 1 machine operator reduces labor costs by 50% annually, and precision cuts waste from 10–15% (manual) to 2–3%—saving $5,000–$10,000/year for mid-sized caterers.
Compliance with global food safety standards is simplified via sealed lines, AI QC, and food-grade materials—critical for winning contracts with schools, hospitals, or multinationals. Flexibility also shines: quick mold changes (30–60 minutes) let businesses switch box sizes or compartment designs (e.g., vegan meals with separate sauces) to adapt to trends.
Space efficiency benefits SMEs too: compact models take up just 10–20 sq. meters (vs. 50–100 sq. meters for traditional lines), with tabletop semi-automatic versions fitting in small commercial kitchens or shared hubs.
Real-World Case: Caterer’s Efficiency Boost
Shanghai-based Green Meal Catering, which serves 12,000 students across 8 schools, struggled with manual production: 6 workers made 3,000 boxes/day in 10-hour shifts, facing late deliveries and high waste. After adopting a semi-automatic machine, the company cut production time to 4 hours/day (with 2 operators), reduced waste from 12% to 2.5%, and passed a government safety audit—winning 3 more school contracts. “The machine paid for itself in 8 months,” says operations manager Li Ming. “We now focus on menu quality, not deadlines.”
Future Trends in Automated Lunch Box Tech
As RTE and catering industries grow, the technology will evolve to support eco-friendly materials (biodegradable PLA, paper-based boxes) aligning with sustainability goals. IoT connectivity will enable remote monitoring (via smartphones) for production speed, maintenance, and inventory. Entry-level semi-automatic models ($15,000–$25,000) will also make automation accessible to micro-SMEs.
For food companies competing in the catering market, automated lunch box making machines offer a clear path to efficiency, safety, and scalability. Whether it's a small lunch box brand or a large institutional catering service provider, this technology can help them meet demand while controlling costs. If you want to learn more, please click on ZHIXIN, we will do our best to help you